Obol vs Other DV Implementations
Table of Contents
Introduction
This document outlines the unique features and advantages of Obol's Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) implementation, comparing it with alternative approaches in the ecosystem. Obol's DVT was specifically designed as a middleware solution to enhance Ethereum's security, resilience, and composability. For a deeper dive into our architectural decisions, check out our blog article Why We Built Charon as a Middleware.
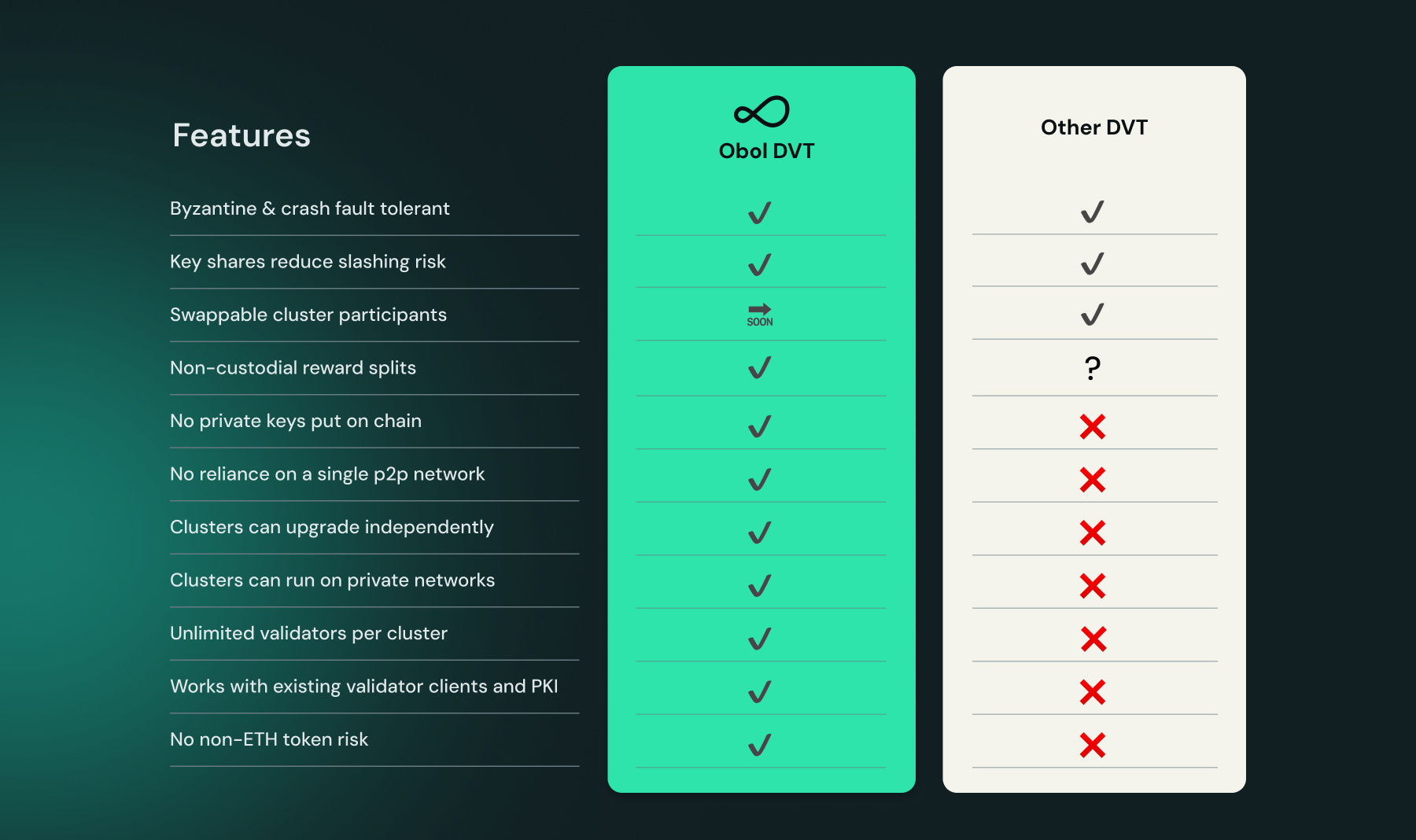
Key Differentiators
No Private Keys Put on Chain
🔐 Enhanced Security Model
Obol's distributed key generation (DKG) process implements a cutting-edge approach to key management:
- Keys are generated locally on participating nodes
- The complete validator key never exists in a single location
- Key shares are distributed securely among cluster participants
- Backup mechanisms are provided for key shares
- Zero exposure of private keys to the internet or blockchain
🚫 Why We Don't Use On-Chain Key Distribution
Some implementations split and encrypt validator keys with node operators' public keys before publishing on-chain. We consider this approach suboptimal because:
- It creates a single point of failure during key generation
- Exposes encrypted private key material to public networks
- Introduces additional attack vectors through the key distribution process
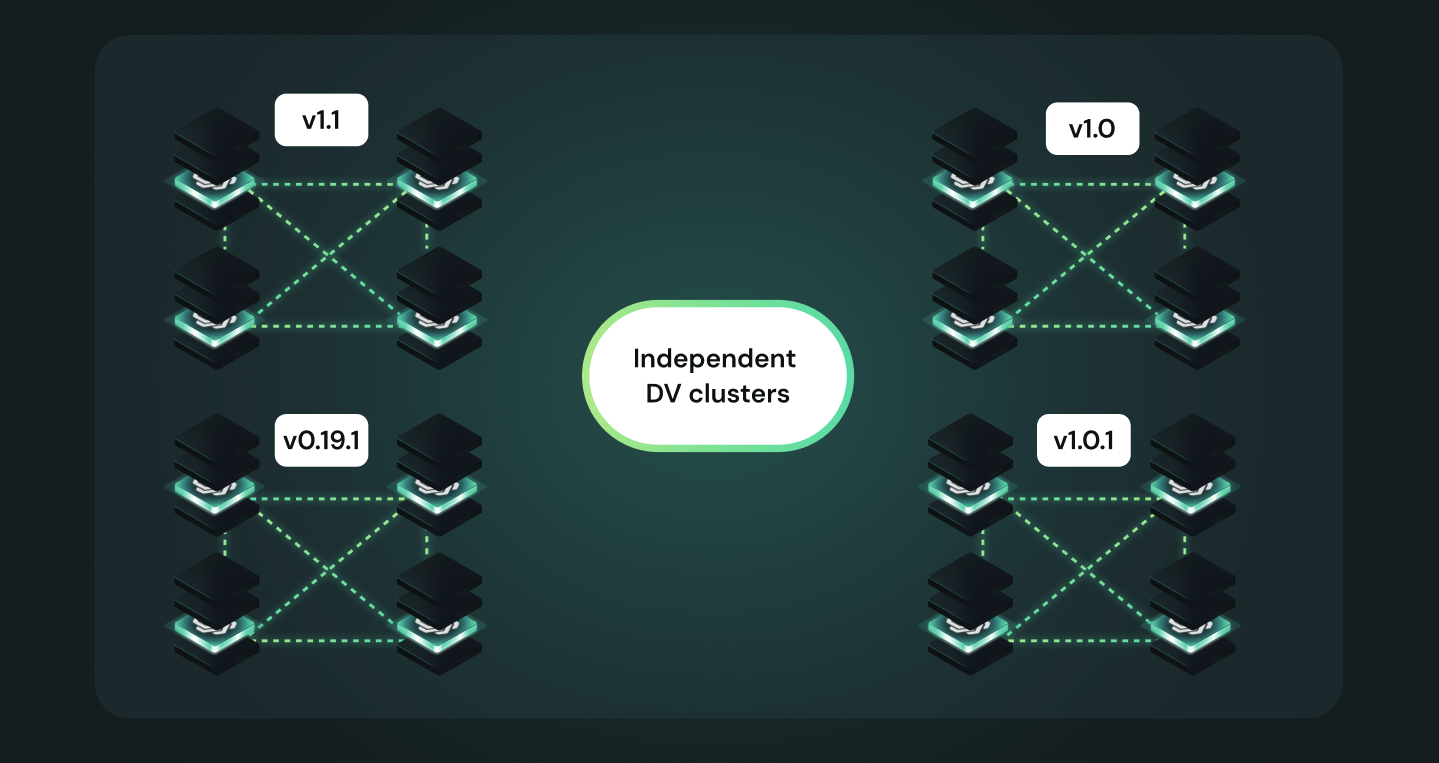
Cluster Independence: Clusters Can Upgrade Independently
🔄 Flexible Upgrade Path
Our architecture enables:
- Independent cluster operations
- Asynchronous version upgrades
- No coordinated hard forks required
- Seamless version compatibility management
Works with Existing Validator Clients and PKI
🔗 Middleware Architecture Benefits
Obol's Charon client:
- Acts as a secure middleware layer
- Preserves existing client infrastructure
- Adds distributed validation capabilities
- Maintains compatibility with standard tools
- Provides additional security through dual validation
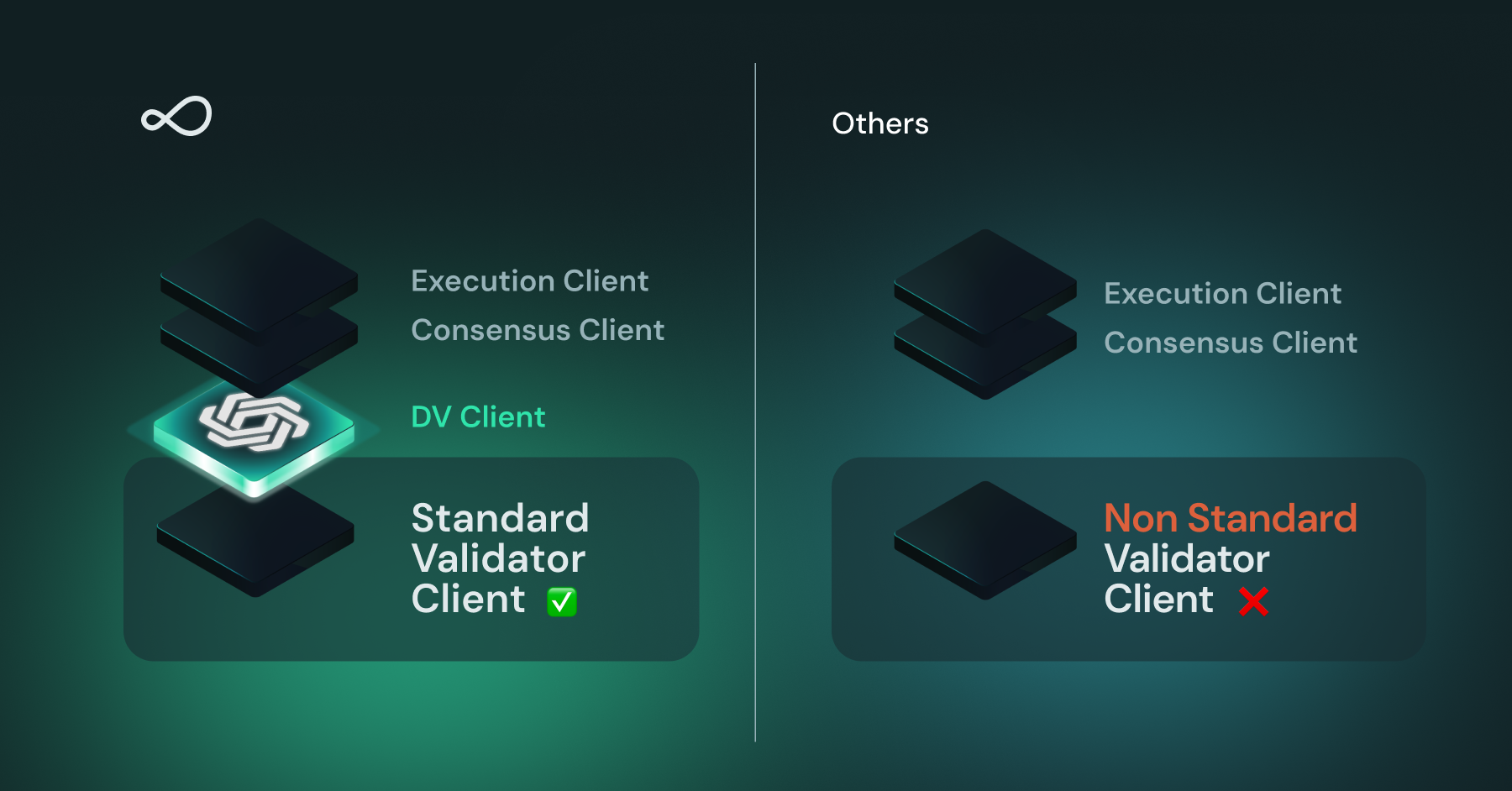
🛡️ Enhanced Security Through Separation
The middleware approach provides multiple advantages:
- Dual validation of signatures
- Protection against supply chain attacks
- Mitigation of remote code execution risks
- Prevention of unauthorized key usage
- Reduced risk of correlated slashing
No Non-ETH Token Risk
💎 Pure ETH Economics
Our implementation:
- Maintains standard 32 ETH validator bonds
- Requires no additional token holdings
- Simplifies economic calculations
- Reduces complexity for operators
- Enables flexible reward distribution

Non-Custodial Reward Splits
💰 Advanced Reward Management
The Obol Splits system provides:
- Clear separation of principal and rewards
- Continuous reward distribution
- Flexible splitting configurations
- Non-custodial operation
- Integration with liquid staking protocols
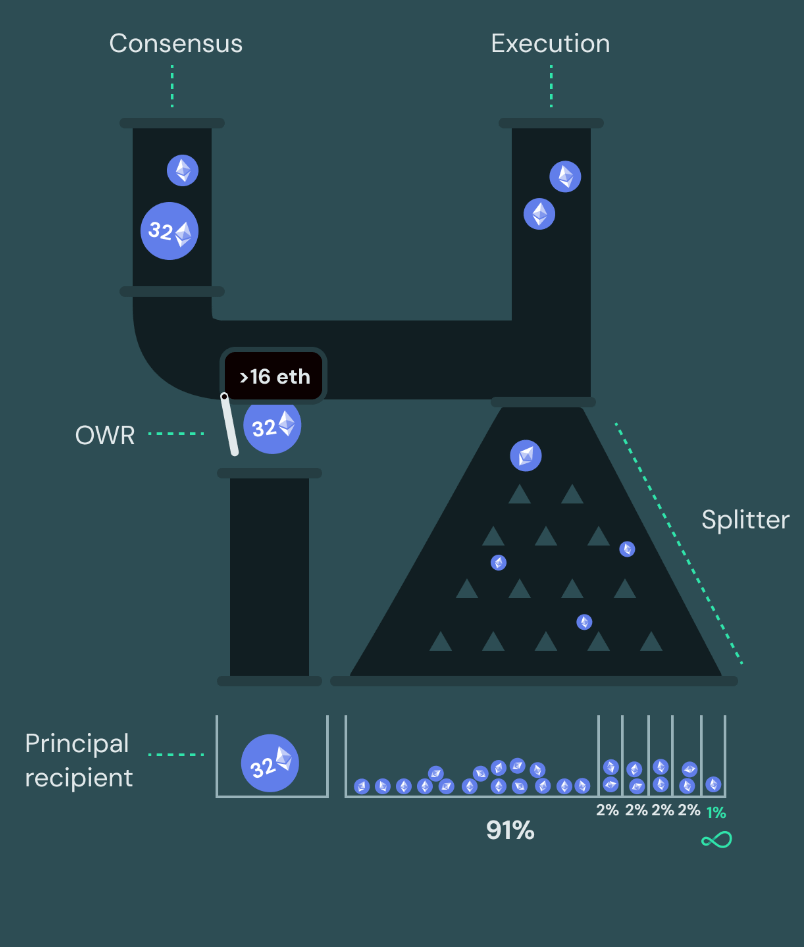
For detailed information about reward distribution, please refer to: